Templates
Form step
Use: DeployedAbout
This is a standardized template for all pages (besides the introduction, review, and confirmation page) of an online form that ask Veterans to enter information, select an answer option, or upload supporting documents. Within Figma, the placeholder section of the form step template is the primary section of the page that you replace with a common form pattern or a custom local component.
Note for designers using the form step template in Figma: You can replace the placeholder with only a single component. You may need to create a custom local Figma component made of multiple design system components or patterns.
View form step template page in VA Figma with padding and accessibility annotations.
Variations
There are two versions of the form step template:
Authenticated
- Includes a header design showing the logged in state
- Includes a prefill information alert near the top of the page that explains to a user that certain information can be prefilled because they are signed in to va.gov. This alert should only appear on pages where information has been prefilled.
- Includes a text area message above the prefill alert notifying a user that their application is saved automatically and provides an ID number.
- Includes a success alert that reiterates when the form autosaves with a timestamp. This success alert only appears after a user interacts with a field. But for design purposes we show it static on all Figma pages.
Unauthenticated
- No authenticated header
- No prefill alert
- No autosave messaging
Example - Authenticated
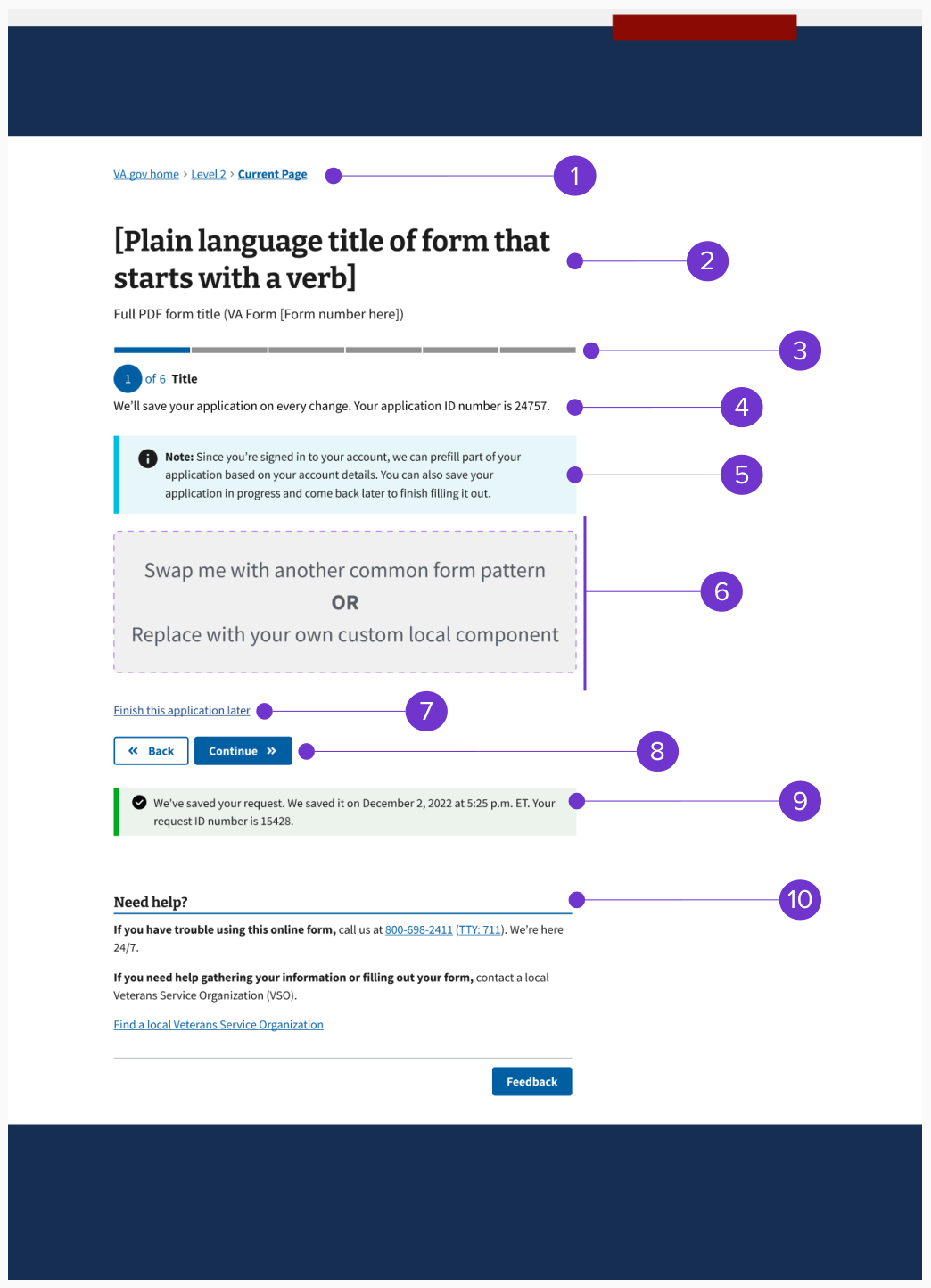
The authenticated form step template consists of:
- Breadcrumb
- Page title and subtitle
- Progress bar - segmented (includes step header)
- Saved as message with application ID
- Prefill alert
- Form step content (includes page title)
- Finish this application later link
- Button pair (Back/Continue)
- Autosave alert
- Need help?
Example - Unauthenticated
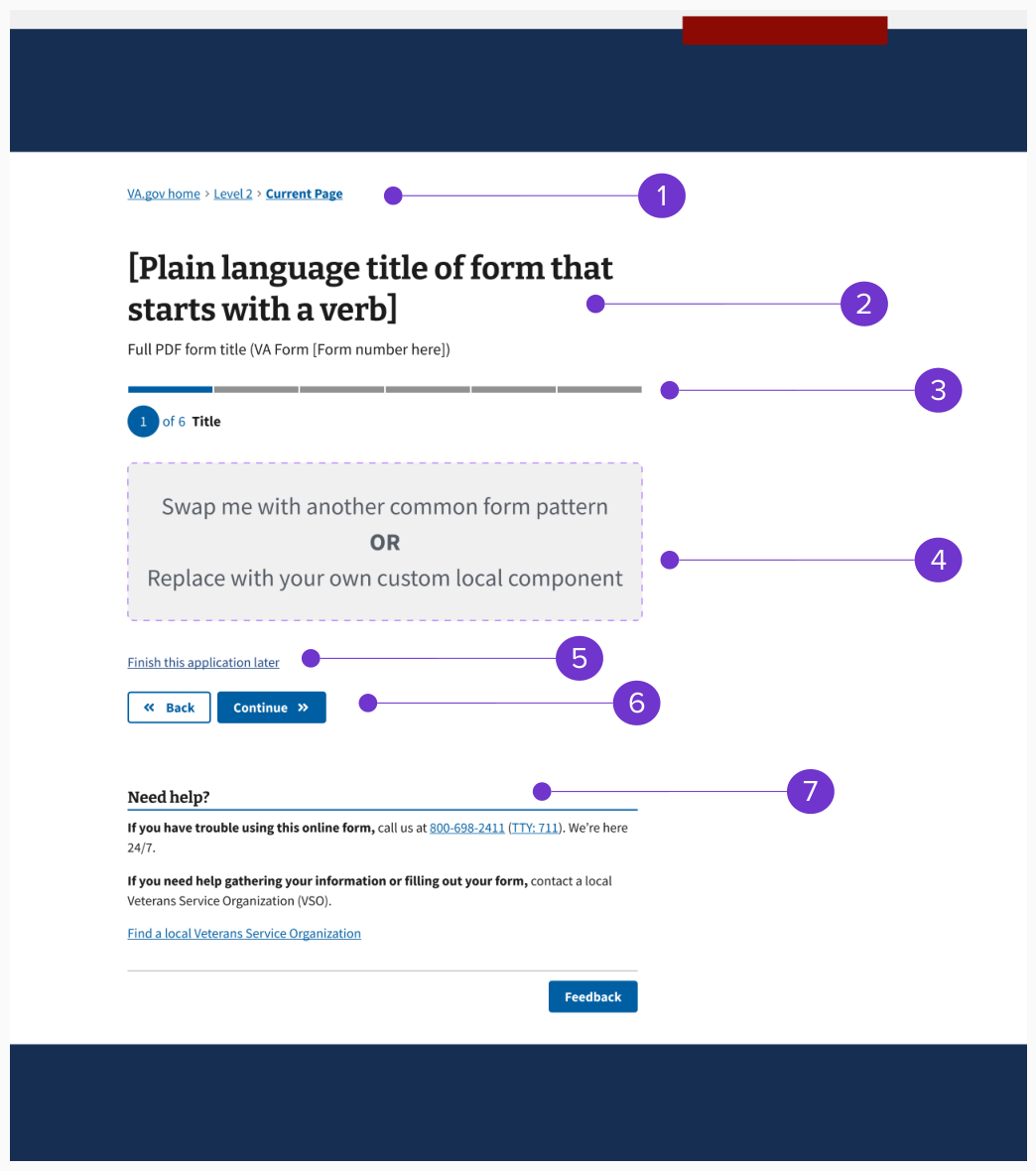
The unauthenticated form step template consists of:
- Breadcrumb
- Page title and subtitle
- Progress bar - segmented (includes step header)
- Form step content (includes page title)
- Finish this application later link
- Button pair (Back/Continue)
- Need help?
Structure
Breadcrumb
The breadcrumb will remain static across all form step pages for a single form. Learn more about expected breadcrumb behavior in the design system. We recommend that designers create a breadcrumb local component in Figma to insert into the form step template rather than manually updating each form step template page individually.
Page title and subtitle
Use the same H1 page title and subtitle as the form introduction, review, and confirmation pages. Review the form introduction template for page title and subtitle for more guidance and examples. We recommend that designers create a page title and subtitle local component in Figma to insert into the form step template rather than manually updating each form step template page individually.
Progress bar & overall form step structure
Use the progress bar - segmented component to organize form steps.
The name for each step within the progress bar is the “step header.” The way you organize the form steps will also impact the “page title” (the H3 that begins the form content section), pattern, and content. A step within the progress bar could, but doesn’t have to, include multiple pages. Because of limitations on the progress bar UI, we recommend limiting all forms to 13 steps total.
The step header should usually have different content than the page title. The step header will be the general type of information you’re collecting (like “Your personal information”) and the page title will be more specific (like “Your name and date of birth”).
If your form contains conditionals, you may need multiple versions of the progress bar to cover all the possible paths (sometimes called user stories) that a user might take through a form. We recommend that designers create a progress bar local component in Figma for each possible path rather than manually updating each form step template page individually.
Crafting thoughtful step headers and page titles
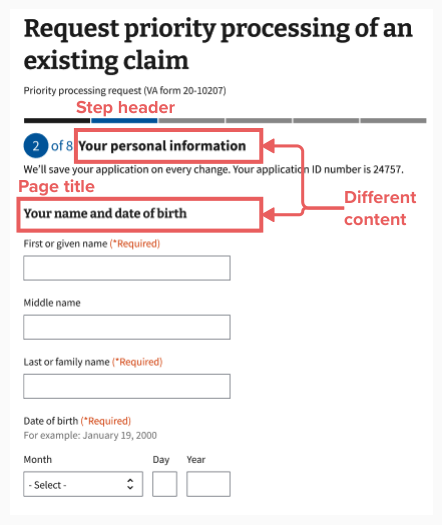
The step header and page title content are important tools to help the person filling out and submitting a form to understand when you’re asking for their information versus another person’s information. Use the step header and the page title to specify the role of the form submitter as needed. For example, use “your” only when referring to the person filling out and submitting the form. Read more in the content style guide about how to use pronouns to promote an active, conversational voice. It is an information architecture best practice to ask for information that is easiest to recall first. Therefore, organize your form to ask for the form submitter’s information first if they are a different person than a Veteran or a non-Veteran claimant.
Identifying within your form’s information architecture who the form submitter is and which pages are asking for their information will also allow you to more easily leverage prefilled information since, as of right now, someone can only be logged in to va.gov as themselves.
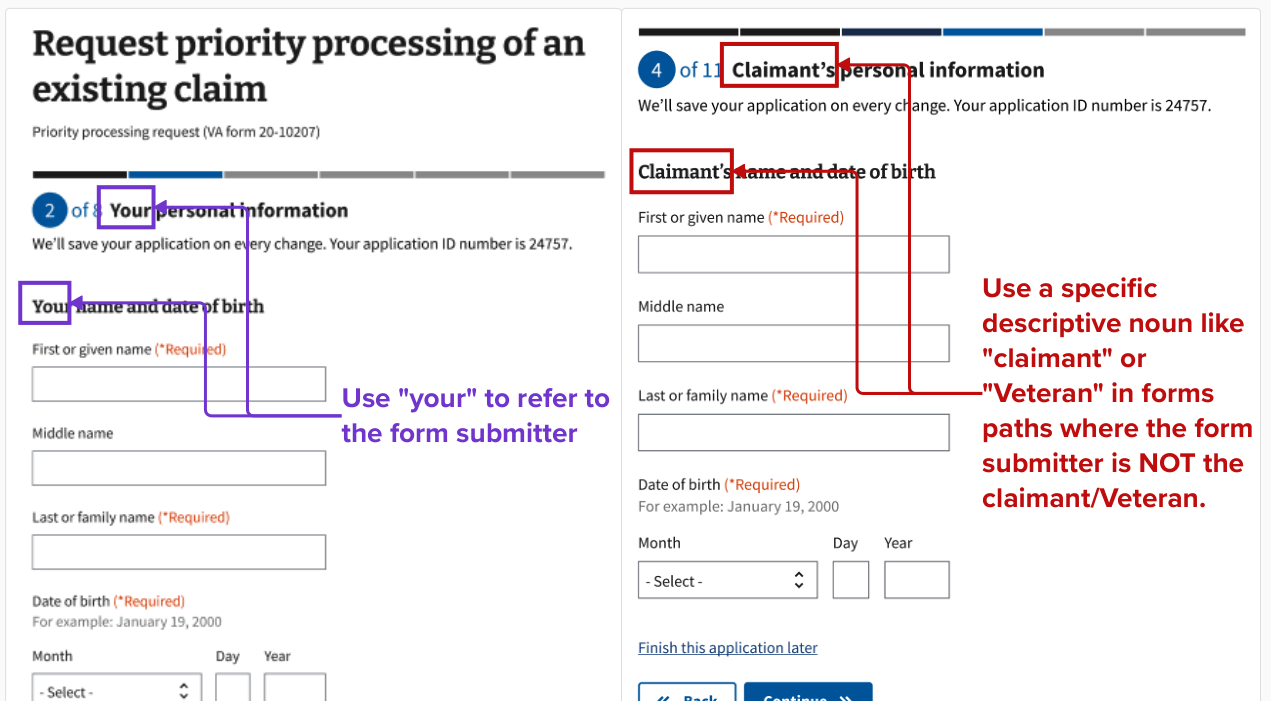
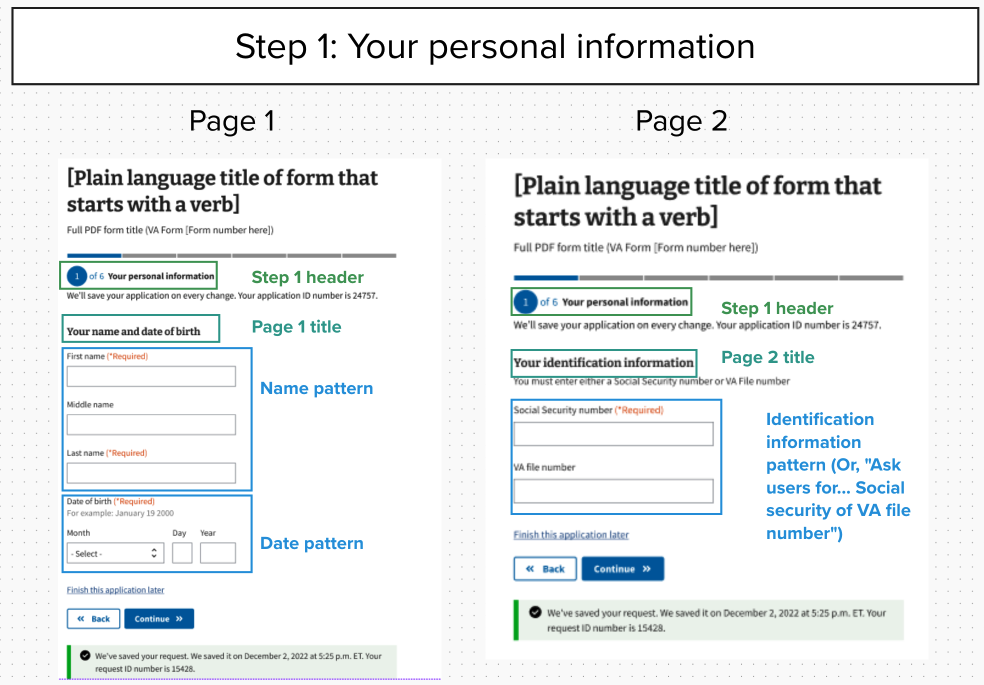
Example of form step structure mockup for form submitter’s personal information step
View an example of the form step structure using mockups for step one. The content of some patterns may be out of date. Notice that this step includes two pages.
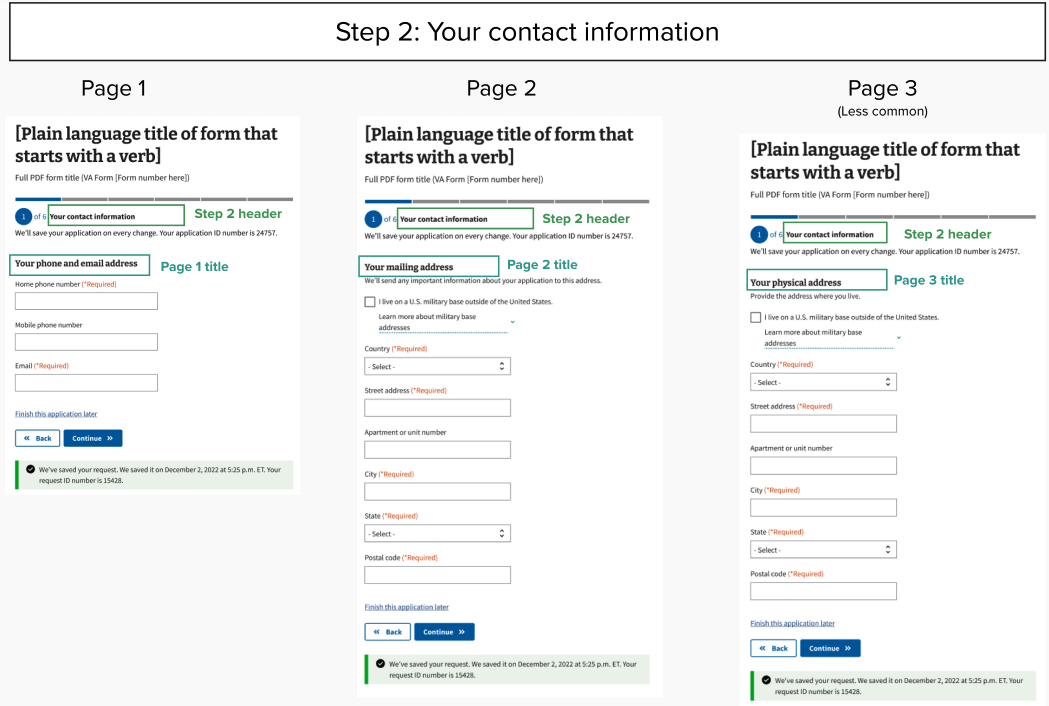
Example of form step structure mockup for form submitter’s contact information step
View an example of the form step structure using mockups for step two. The content of some patterns may be out of date. Notice that this step includes three pages.
Saved as message with application ID
Text area notifying a user that their application is saved automatically and provides an application ID number.
Form step content
Insert customized form step content in this section of the form step template. Consult the form step structure guidance above and the One thing per page design principle to determine how much form content to fit onto a single page.
Some components may include the option to add body text, hint text, or additional information. Use these guidelines to decide which one to use.
Body text
Use body text to add clarifying information that is relevant to all the information under a page title. The body text should either clarify what type of information we need, or explain what we’re going to do with the data. Aim for fewer than fifty words in the body text. If you need more space, consider moving nonessential information to an additional info component.
Hint text
Add hint text under a field label if it would help someone choose the right response to give–like “We’ll use your email address to confirm when we receive your form” since knowing how we’ll use their email may help them choose which email to enter. Or use hint text to help someone answer a question more easily–like “For example: January 1, 2001”. Don’t use punctuation in hint text unless the copy is two sentences or more.
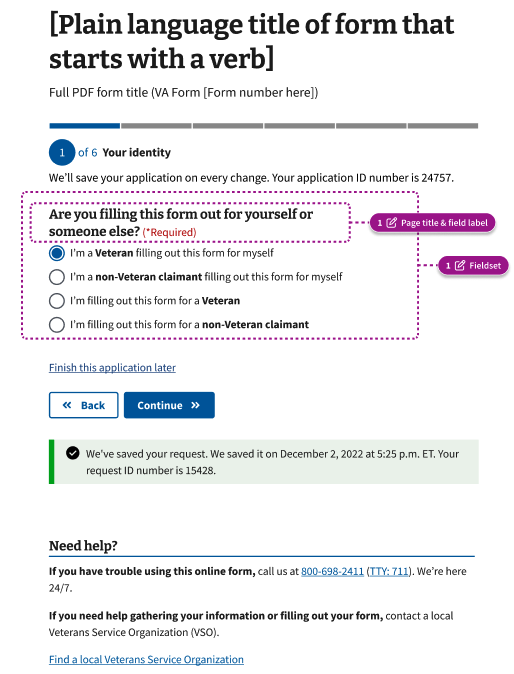
Field label text (also called legend)
On a form step page with only one question, you must create a separate page title and field label (also called the legend). The exceptions to this rule are that the page title could also be the field label ONLY for a checkbox or radio group. For example, the radio button question “Are you filling this form out for yourself or someone else?” is both the page title and field label.
Additional information
Use the additional information component if there’s relevant information that may be important for some people, but it’s not critical information for everyone filling out the form. Review guidelines for using the additional information component.
Finish this application later link
A link that allows the user to exit the process with their progress saved.
Button pair
Button pair contains a secondary button labeled “Back” and primary button labeled “Continue”. On the last form step page, change “Continue” to “Submit”.
Autosave alert
The Autosave component provides the last saved date and time in a Alert - background only - Success variation. A related line of text just under the step header also tells users that we’ll save their form after every change. This only shows to authenticated users.
Need help?
The Need help? component appears on the bottom of every page of the form. This content tells users how to get additional help with the form or contact VA about their related benefits. You can customize the content for the specific form.